

Second, the cytotoxic drug DM1 and its metabolites cause off-target toxicity to surrounding cells, i.e., inhibition of cell mitosis and cell cycle arrest, due to separation from the monoclonal antibody component after internalization ( 7, 8). Although the expression of the HER2 antigen on tumors is higher than that on normal tissues, clinical studies have demonstrated that the success of ADCs depends on the targeting technology ( 6). the expression of HER2 in normal tissues such as the lung and gastrointestinal tract may not only reduce the delivery of ADCs to tumors, but also more importantly cause on-target off-tumor toxicity. The HER2 antigen is the tumor-targeting binding site of the ADC, and its distribution in vivo seems to determine the target of ADC toxicity. First, targeted nontumor toxicity is caused by the extensive expression of the HER2 antigen in normal tissues. There a variety of mechanisms of toxicity.
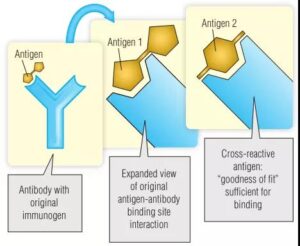
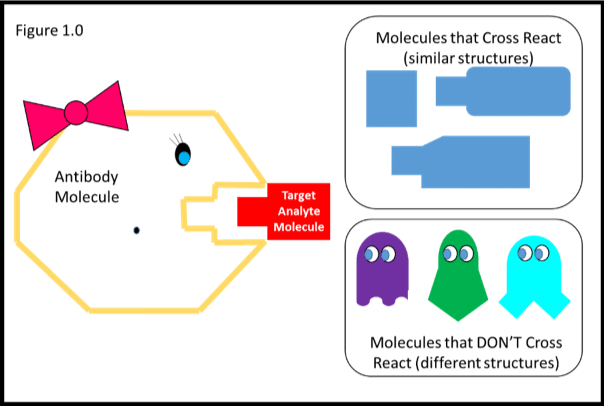
#PRIMARY ANTIBODY CROSS REACTIVITY SERIES#
However, although the monoclonal antibody component of the ADC enhances the targeting of cytotoxic DM1 and theoretically reduces its toxic effects on normal tissues, ADCs have shown a series of side effects in clinical and nonclinical studies ( 5). Since DM1 is selectively released into tumor cells and has a lower killing effect on normal cells, CPGJ701 should be more targeted and safer than DM1 alone. The ADC is enzymatically lysed in lysosomes, and releases the toxins DM1, which disrupts the stability of the intracellular microtubules of tumor cells, leading to tumor cell cycle arrest and apoptosis ( 4).
The mechanism of action is that the antibody component of the ADC is targeted to bind to the extracellular HER2 domain on the surface of tumor cells and enter the tumor cells by endocytosis. CPGJ701 consists of an antibody, a chemical linker, and a DM1, the cytotoxic tubulin inhibitor DM1 is conjugated to a targeted HER2 antibody via a chemical linker ( 2, 3). Recombinant humanized anti-human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2) monoclonal antibody-derivative of the cytotoxic agent maytansine (DM1) conjugate (CPGJ701) is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) for the treatment of HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer ( 1).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
